Bile Imbalance Linked to Liver Cancer: Key Findings
Bile imbalance linked to liver cancer has emerged as a crucial area of research, particularly concerning hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most prevalent type of liver cancer. Recent studies indicate that disruption in bile acid production can lead to significant liver damage, inflammation, and eventually cancer. This critical relationship between bile acids and liver health highlights the importance of understanding FXR signaling, as it plays a vital role in maintaining bile acid homeostasis. Discovering how this imbalance triggers liver cancer has vast implications for liver cancer treatment, opening avenues for innovative therapeutic strategies. As researchers delve deeper into HCC research, they aim to identify targeted interventions that could prevent or mitigate the onset of this devastating disease.
In the realm of hepatic disease, a disruption in bile flow and composition is increasingly recognized as a precursor to serious conditions, notably liver malignancies. Hepatocellular carcinoma, the leading form of liver cancer, can be exacerbated by irregularities in bile acids, substances essential for fat digestion that also exert regulatory effects on various metabolic pathways. Recent insights into FXR signaling, a key molecular pathway governing bile homeostasis, reveal promising avenues for innovative liver cancer treatment approaches. By studying how altered bile dynamics contribute to liver pathology, researchers are paving the way for novel strategies aimed at combating this severe organismal affliction. Enhanced focus on bile management in the context of liver health could yield significant advancements in HCC research and patient outcomes.
Understanding Bile Imbalance and Liver Cancer
Bile imbalance is increasingly recognized as a significant factor in the development of liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The liver’s ability to regulate bile acid production is not only critical for digestion but also for maintaining metabolic balance in the body. When this delicate balance is disrupted, it can lead to elevated bile acid levels, which have been linked to liver injury, inflammation, and eventually cancer. Current research highlights the role of FXR signaling, a key regulatory pathway that maintains bile acid homeostasis; disruptions in this pathway can promote disease progression.
Recent studies illustrate the intricate relationship between bile acids and liver cancer treatment strategies. By identifying molecular switches that modulate bile acid levels, researchers can devise novel therapeutic interventions for HCC. This could involve enhancing FXR activity or promoting bile acid excretion, pivotal approaches that could mitigate the toxic buildup associated with bile imbalance. Understanding these mechanisms allows for more targeted liver cancer treatments, potentially improving patient outcomes.
Key Molecular Mechanisms Behind Bile Acids and HCC
At the heart of the relationship between bile acids and liver cancer lies the molecular mechanism involving the YAP protein. Research led by Yingzi Yang uncovered that YAP not only influences cell growth but also plays a crucial role in regulating bile acid metabolism. When YAP is activated, it inhibits the FXR receptor’s function, leading to excessive bile acid production and accumulation. This process heightens the risk of fibrosis, inflammation, and ultimately hepatocellular carcinoma, emphasizing the need for comprehensive understanding of these pathways.
The implications of targeting YAP and FXR signaling pathways in liver cancer treatment are profound. By potentially blocking YAP’s repressive activity or enhancing FXR’s functionality, new therapeutic avenues may emerge to combat liver damage and slow cancer progression. Additionally, ongoing HCC research aims to identify pharmacological agents that can activate FXR or promote bile acid export, which might represent groundbreaking strategies in the fight against liver cancer.
The Role of FXR Signaling in Liver Cancer Therapy
FXR signaling plays a pivotal role in the maintenance of bile acid levels and overall liver health. Recent findings suggest that activating the FXR receptor can offer protective effects against liver damage and could slow the progression of HCC. By enhancing FXR signaling, not only can the toxic accumulation of bile acids be reduced, but the associated inflammatory responses that contribute to the development of liver cancer may also be mitigated. This highlights the therapeutic potential of FXR activators in liver cancer treatment.
In the context of hepatocellular carcinoma, the ability to manipulate FXR signaling represents a promising strategy in developing new treatments. By focusing on pharmacological solutions that stimulate FXR and promote bile acid export, researchers aim to disrupt the cycle of bile acid accumulation and its deleterious effects on the liver. This approach could open doors to innovative intervention strategies that could significantly improve the prognosis for patients battling liver cancer.
Research Advancements in Bile Acid Metabolism
Research into bile acid metabolism has advanced significantly in recent years, revealing crucial insights into its role in liver health and disease. The identification of molecules such as YAP and their impact on bile acid regulation has propelled understanding of their contribution to liver cancer pathogenesis. Understanding how these molecular players interact not only clarifies the underlying mechanisms of disease but also provides potential targets for therapeutic strategies.
Continuous HCC research is focused on exploring the relationship between bile acids and metabolic control, thereby uncovering how disturbances in bile acid homeostasis can initiate a cascade leading to cancer. As studies progress, the hope is that new treatments will emerge, targeting these metabolic pathways to prevent and treat liver cancer effectively. The commitment to understanding bile acid dynamics in the context of liver cancer is crucial for developing holistic treatment approaches.
Implications of Bile Imbalance for Liver Health
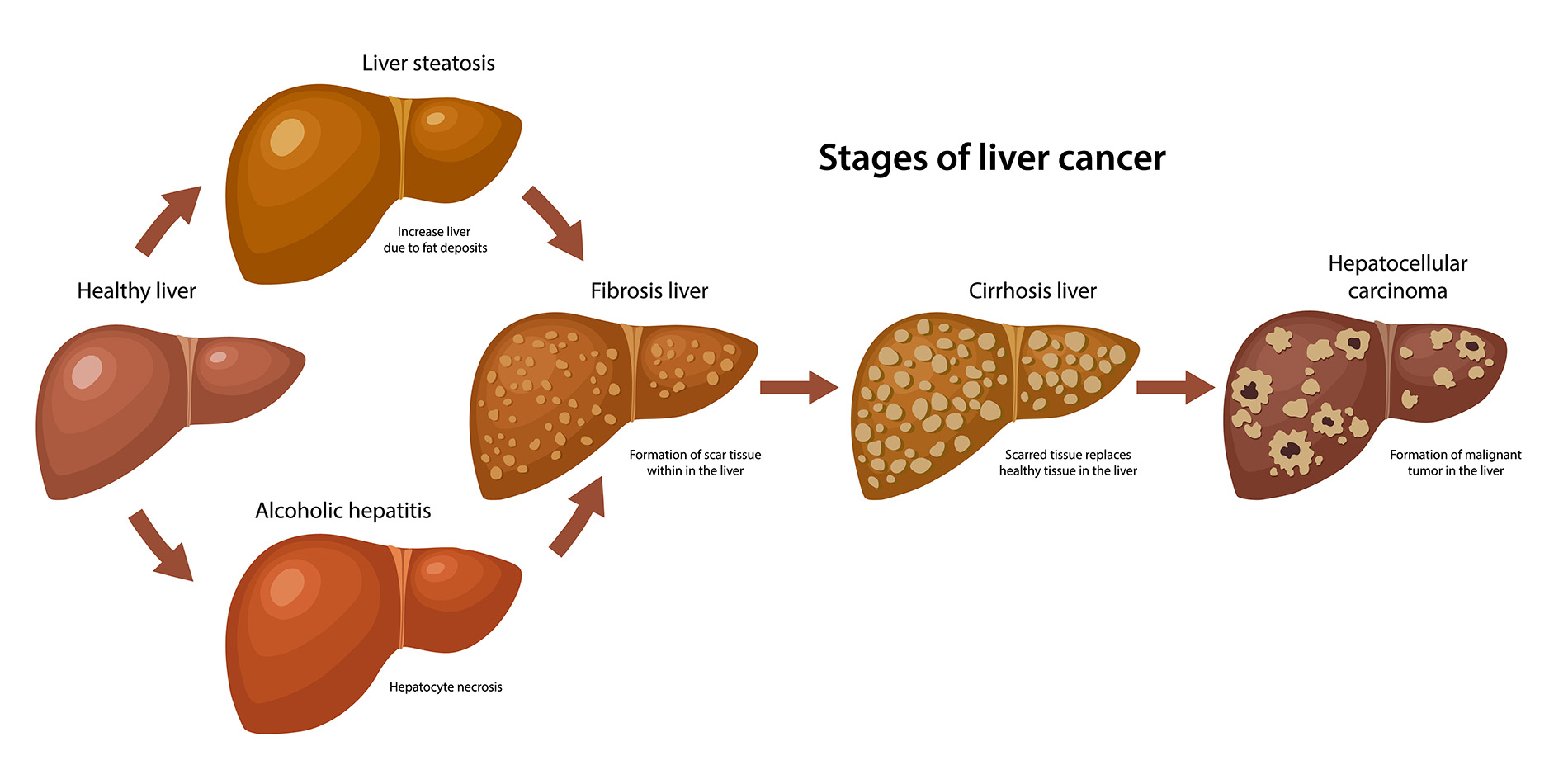
The implications of bile imbalance extend beyond liver cancer and can impact overall health significantly. Disruptions in bile acid levels can lead to a variety of liver-related disorders, including fatty liver disease and cholestasis. These conditions often precede hepatocellular carcinoma, highlighting the importance of early detection and intervention in preserving liver function and preventing cancer development.
Recognizing the signs of bile acid imbalance is crucial for healthcare practitioners. By employing comprehensive assessments and monitoring bile acid levels, effective early interventions can be deployed, preventing the progression to more severe liver disease or cancer. This proactive approach could save lives and improve the quality of care for individuals at risk of developing liver-related issues.
Current Trends in Liver Cancer Treatment
Liver cancer treatment has witnessed remarkable advancements in recent years, with a focus on personalized medicine and targeted therapies. As research unravels the complex biology of HCC, treatments are increasingly being tailored to individual patient needs. Strategies include combining traditional methods such as surgery and chemotherapy with targeted therapies that address specific molecular pathways, including bile acid metabolism.
Moreover, the integration of innovative therapies targeting FXR signaling and bile acid homeostasis marks a significant shift in the treatment landscape. By leveraging insights from current research, healthcare providers can offer a more comprehensive approach to liver cancer management, improving patients’ chances of survival and enhancing their quality of life. Such progress underscores the importance of ongoing research efforts to continue developing effective treatments.
The Future of Research in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
The future of research in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is poised to explore new frontiers, particularly in understanding the intricate relationship between bile acids and cancer development. Scientists are focusing on the molecular pathways that govern bile acid metabolism, aiming to develop innovative therapies that can combat liver cancer effectively. This line of inquiry is essential as it offers hope for better outcomes through targeted interventions.
Moreover, the emphasis on collaboration between researchers, clinicians, and pharmaceutical developers will play a significant role in accelerating the translation of laboratory findings into clinical applications. Advancements in genomic and cellular technologies hold tremendous potential to unveil novel targets for liver cancer treatment, ensuring that future patients benefit from cutting-edge therapies derived from the latest scientific discoveries.
Strategies for Enhancing Bile Acid Homeostasis
Enhancing bile acid homeostasis is crucial for preventing liver damage and reducing the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. One promising strategy involves the use of FXR agonists, compounds that can activate the FXR receptor, effectively promoting bile acid metabolism and excretion. This intervention could help restore balance, mitigating the detrimental effects of bile acid accumulation that contribute to liver disease development.
Additionally, lifestyle modifications such as diet and exercise can play a supportive role in enhancing bile acid homeostasis. By promoting a healthy diet rich in fiber and healthy fats, individuals can naturally aid bile metabolism and support liver health. Education on the importance of maintaining bile balance could serve as a cornerstone in preventive strategies against liver-related diseases and cancer.
The Link Between Bile Acids and Metabolic Disorders
The relationship between bile acids and metabolic disorders is increasingly recognized, particularly in the context of liver health. Bile acids not only aid in digestion but also serve as signaling molecules that influence various metabolic pathways. Disruptions in bile acid homeostasis can lead to metabolic dysregulation, increasing the risk for conditions such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, and, subsequently, hepatocellular carcinoma.
Understanding these connections is vital for developing comprehensive treatment strategies that address both liver health and metabolic conditions. In the realm of HCC research, exploring the role of bile acids in metabolic control could provide insights into new interventions that target not only cancer but also the underlying metabolic disorders that contribute to liver disease.
Frequently Asked Questions
What role does bile imbalance play in liver cancer development?
Bile imbalance is critical in liver cancer development, particularly in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Disrupted bile acid regulation leads to liver injury, inflammation, and ultimately cancer progression. Excessive bile acids accumulate in the liver when key regulatory pathways, like FXR signaling, are inhibited, promoting conditions that favor tumor formation.
How can bile acids influence liver cancer treatment strategies?
Bile acids have a dual role in liver metabolism and disease. Research indicates that targeting the farnesoid X receptor (FXR) can enhance bile acid regulation, potentially offering novel liver cancer treatment strategies. By activating FXR or promoting bile acid excretion, therapies could mitigate liver damage and slow down HCC progression.
What recent research has been published about bile imbalance in liver cancer?
A recent study published in Nature Communications reveals how a molecular switch regulating bile acids contributes to liver cancer. The study uncovers that YAP, a signaling pathway component, represses FXR function, which disrupts bile acid homeostasis, leading to liver fibrosis and HCC. This research is pivotal for developing targeted liver cancer treatments.
What is the significance of FXR signaling in bile acid metabolism and liver cancer?
FXR signaling is essential for maintaining bile acid homeostasis. Its inhibition by the YAP pathway leads to excessive bile acid production, resulting in liver inflammation and cancer. Targeting FXR signaling could offer new therapeutic avenues for liver cancer by restoring bile acid balance and preventing tumor development.
Can lifestyle changes impact bile acid balance and liver cancer risk?
Yes, lifestyle changes can influence bile acid balance and potentially reduce liver cancer risk. A healthy diet, regular exercise, and weight management support liver health and improve bile acid metabolism, which may help mitigate the development of liver diseases, including HCC.
What are the potential therapeutic implications of targeting YAP in liver cancer?
Targeting YAP in liver cancer offers promising therapeutic implications by reversing its repressive effects on FXR. Enhancing FXR function or increasing bile acid excretion could disrupt the tumorigenic process linked to bile acid imbalance, paving the way for innovative liver cancer treatments.
How does bile acid imbalance relate to liver injury and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)?
Bile acid imbalance results in liver injury through mechanisms such as inflammation and fibrosis, creating a conducive environment for the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The dysregulation of bile acids, particularly their overproduction, can exacerbate liver conditions that lead to cancer.
What are the research prospects for bile acids and liver cancer interventions?
Ongoing research into bile acids and liver cancer interventions focuses on understanding the role of FXR and YAP signaling. Studies aim to develop pharmacological solutions that stimulate FXR activity or enhance bile acid excretion, showcasing potential for innovative approaches in liver cancer treatment.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Bile Imbalance and Liver Cancer | A critical imbalance in bile acids produced by the liver can trigger liver diseases, notably hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most common form of liver cancer. |
| Key Molecular Switch Identified | The study identifies a key molecular switch that regulates bile acids, offering insights into potential treatment interventions for liver cancer. |
| Role of Bile Acids | Bile acids have multiple functions, including aiding fat digestion and regulating metabolic processes in the body. |
| Impact of YAP on Bile Acid Regulation | YAP inhibits FXR, a crucial bile acid sensor, leading to an excess of bile acids in the liver that contributes to inflammation and fibrosis. |
| Potential Treatment Strategies | Enhancing FXR function or increasing bile acid excretion could disrupt the cycle of bile acid overproduction and liver cancer progression. |
| Research Support | The Yang Laboratory’s research was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the National Cancer Institute. |
Summary
Bile imbalance linked to liver cancer is a critical issue raised by recent studies, revealing how disruptions in bile acid production can lead to severe liver diseases including hepatocellular carcinoma. Understanding the mechanisms behind bile acid regulation could open up new pathway for effective treatments, highlighting the importance of ongoing research in this area.