Pregnancy-Related Deaths: Alarming Rise in the U.S.
Pregnancy-related deaths are an alarming public health issue in the United States, where maternal mortality rates continue to rise despite being largely preventable. A recent study reveals that more than 80% of these deaths could have been avoided with better prenatal care and systemic healthcare improvements. The U.S. leads high-income countries in maternal mortality, reflecting significant health disparities among different racial and ethnic groups. Factors such as inadequate postpartum care and a fragmented public health infrastructure contribute profoundly to this crisis. Addressing these issues is crucial to ensuring the health and safety of pregnancies across the nation.
The term “maternal mortality” encompasses a critical facet of public health that highlights the risks associated with childbirth, particularly evident in recent statistics surrounding pregnancy-related fatalities. This unfortunate rise in deaths emphasizes the need for enhanced healthcare strategies before, during, and after pregnancy. By considering the broader context of reproductive health, including prenatal and postpartum care, we can better understand the underlying health disparities that contribute to these fatalities. Furthermore, a renewed focus on equity within our public health infrastructure is necessary to address these alarming trends. Effective solutions must be implemented to safeguard maternal health and reduce mortality rates across diverse populations.
The Rising Concern of Pregnancy-Related Deaths in the U.S.
The alarming increase in pregnancy-related deaths in the United States highlights a critical public health issue that demands immediate attention. From 2018 to 2022, the maternal mortality rate rose significantly, reaching 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births by 2022, compared to 25.3 in 2018. This trend is particularly concerning as over 80% of these fatalities are preventable, suggesting a failure in the healthcare system to provide adequate prenatal and postpartum care. The data presented by researchers indicate blatant disparities influenced by race, ethnicity, and geography, underscoring the necessity for systemic reforms.
In many cases, access to quality prenatal care is inconsistent across various regions, contributing to these disparities. Maternity care deserts exist where expectant mothers struggle to receive the healthcare they need, particularly in high-risk populations. Addressing the rise in pregnancy-related deaths requires not only an overhaul of medical practices but also a concerted effort to understand and rectify the social determinants of health that leave many women vulnerable during and after pregnancy.
Understanding Maternal Mortality: Key Causes and Prevention Strategies
Maternal mortality, as a public health challenge, has complex roots intertwined with various health conditions, primarily cardiovascular diseases that are now leading contributors to pregnancy-related deaths. According to the study, cardiovascular complications accounted for over 20% of these fatalities. With the increasing prevalence of chronic health issues such as hypertension in younger populations, it is crucial to focus on enhancing prenatal care that includes thorough screenings and education on managing these risks effectively throughout pregnancy.
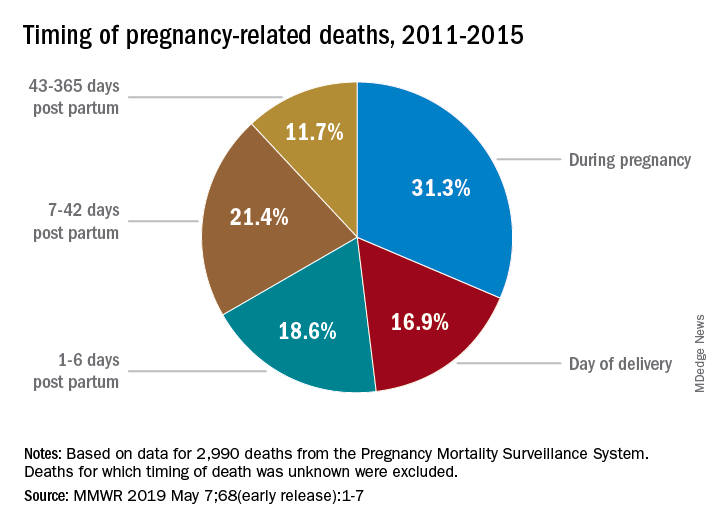
Moreover, pregnant individuals need continuous care that extends beyond the traditional six-week postpartum period. Late maternal deaths, occurring between 42 days and one year after childbirth, account for nearly a third of total maternal fatalities. This statistic emphasizes the importance of an inclusive healthcare approach during the entire postpartum period, suggesting that systemic changes should aim at providing comprehensive care throughout pregnancy and into the recovery phase.
Health Disparities in Maternal Health Outcomes
The disparities in maternal health outcomes are stark and alarming, as demonstrated by the significant variations in pregnancy-related deaths across different races and states. For instance, American Indian and Alaska Native women face maternal mortality rates nearly four times higher than white women, pointing to entrenched inequities in healthcare access and outcomes. Public health strategies must therefore address these disparities by catering to the unique needs of various racial and ethnic groups.
Intersecting factors such as socioeconomic status, education, and geographical location significantly influence a woman’s access to effective prenatal and postpartum care. Policies aimed at mitigating these disparities must include targeted funding for community-based health initiatives, outreach programs, and education campaigns that foster awareness about maternal health risks, particularly in underserved populations.
The Role of Public Health Infrastructure in Maternal Care
The integrity of public health infrastructure is fundamental to improving maternal healthcare outcomes in the U.S. Unfortunately, the data suggests a lack of investment in public health strategies, which is essential for tracking, addressing, and ultimately reducing pregnancy-related deaths. With significant cuts to research funding and public health initiatives, the capacity to analyze and improve maternal health is under threat. Therefore, it’s imperative to prioritize the strengthening of this infrastructure to ensure comprehensive maternal health policies are enacted.
Investing in robust public health systems not only aids in better tracking of pregnancy-related deaths, but also equips states with the necessary resources to implement effective healthcare solutions. Such investments could facilitate innovations in prenatal care and enhance postpartum support, creating pathways to significantly lower maternal mortality rates and address the inequalities that persist across the country.
Enhancing Prenatal and Postpartum Care for Better Outcomes
Optimizing prenatal and postpartum care is central to the discourse on preventing maternal mortality. Comprehensive prenatal care includes regular check-ups, screenings for potential health problems, and education on nutrition and wellness during pregnancy to mitigate risks. Moreover, extending postpartum care beyond six weeks to monitor and address any health complications can significantly lower the rates of late maternal deaths, creating a continuum of care that supports women throughout the entire motherhood journey.
Effective communication and education within healthcare systems are also vital. Healthcare providers must foster an environment that encourages expectant mothers to voice their health concerns openly, thereby enabling more personalized care. This approach not only acknowledges the diverse experiences of women during pregnancy but also enhances the quality of care provided, further reducing the likelihood of preventable deaths.
Investing in Innovative Solutions to Improve Maternal Health
As the study indicates, there is an urgent need for innovation within the maternal healthcare landscape to combat rising pregnancy-related deaths. Investing in technology that enables better monitoring of pregnant individuals, along with establishing better communication systems between patients and healthcare providers, can significantly improve outcomes. Tools such as telehealth can facilitate easier access to care, especially in rural and underserved areas where traditional maternal health services may be lacking.
Incorporating evidence-based practices and solutions that target quality improvement in maternal health is also essential. This can involve using data analytics to identify high-risk pregnancies early and creating tailored care plans that address specific needs. By fostering a culture of innovation and responsiveness in maternal care practices, the healthcare industry can more effectively tackle the complex factors contributing to maternal mortality.
The Importance of Addressing Social Determinants of Health
To effectively reduce rates of maternal mortality, it’s crucial to tackle the broader social determinants of health that underlie many disparities faced by different demographics. These determinants include factors such as income level, education, access to healthcare, and even the availability of community resources that directly impact a woman’s ability to seek and obtain quality prenatal and postpartum care. Addressing these factors can help create an equitable healthcare system where every woman has the opportunity to receive the care she needs.
Community engagement and education initiatives can play an essential role in bridging these gaps. By empowering women with knowledge and resources about their health and the maternal care system, communities can help reduce barriers to accessing necessary services. Advocacy efforts must also be directed toward enhancing public policies that support maternal health equity, thereby fostering an environment where mothers are safer and healthier throughout their pregnancy and beyond.
Collaborative Approaches to Tackling Maternal Health Inequities
Collaboration among various sectors of society is essential to address the multifaceted issue of maternal mortality and its preventable deaths. Stakeholders such as healthcare providers, community organizations, policymakers, and public health advocates must work together to create comprehensive strategies aimed at improving maternal health outcomes. This collaborative effort can enhance the effectiveness of interventions designed to minimize health disparities and promote access to quality care for all pregnant individuals.
Initiatives such as statewide maternal health coalitions can facilitate coordinated efforts to share resources, research, and best practices among healthcare systems. By aligning objectives and mobilizing community resources, these coalitions can develop tailored action plans that address specific regional challenges in maternal care, leading to more effective and equitable health outcomes for mothers across diverse populations.
Rethinking Maternal Health Policy for Future Generations
Rethinking maternal health policy in the U.S. involves not just immediate investments but also long-term commitment to structural changes in how maternal care is approached. Policymakers must recognize the urgency to shift towards preventative care models that emphasize health education, early intervention, and comprehensive support systems that span before, during, and after pregnancy. This strategic shift is necessary to create sustainable health policies that holistically address the needs of mothers, thereby reducing maternal mortality rates.
Furthermore, including women’s voices in policymaking can lead to more relevant and effective maternal health policies. Engaging with mothers and health professionals can provide invaluable insights into the challenges they face, guiding the development of policies that are responsive to those needs. By ensuring that maternal health policies are inclusive and representative, the U.S. can work towards achieving health equity and reducing preventable pregnancy-related deaths.
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors contribute to the high rate of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. compared to other high-income countries?
The U.S. has a high rate of pregnancy-related deaths due to a fragmented healthcare system, policies that create inequities, and insufficient maternity care, particularly in underserved areas. Additionally, chronic health conditions like cardiovascular disease are increasingly affecting younger women, further exacerbating maternal mortality rates.
How do health disparities influence pregnancy-related mortality rates among different racial groups?
Health disparities significantly affect pregnancy-related mortality, with American Indian and Alaska Native women experiencing the highest rates. Systemic bias and discrimination in healthcare access and quality continue to perpetuate these disparities across racial and ethnic groups, highlighting the need for targeted public health interventions.
Why is postpartum care crucial in reducing pregnancy-related deaths?
Postpartum care is essential as nearly one-third of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. occur between 42 days and one year after childbirth. Extended support during the postpartum period can address ongoing health issues that might lead to maternal mortality. Acknowledging this timeframe emphasizes the need for comprehensive postpartum care, which is often neglected.
What role does public health infrastructure play in addressing pregnancy-related deaths?
An effective public health infrastructure is vital for tracking pregnancy-related deaths and implementing policies aimed at improving maternal health outcomes. Investment in data collection, research, and quality care initiatives can help reduce the preventable deaths associated with pregnancy and highlight the disparities among different populations.
How does prenatal care impact the rates of pregnancy-related mortality?
Quality prenatal care is crucial for monitoring and managing health risks during pregnancy, which can directly lower the rates of pregnancy-related mortality. Ensuring access to comprehensive prenatal services helps identify and address medical conditions early, preventing complications that could lead to maternal deaths.
What measures can be taken to decrease the incidence of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S.?
To reduce pregnancy-related deaths, it is essential to invest in healthcare policies that promote equitable prenatal and postpartum care, enhance public health infrastructure, and increase awareness of maternal health issues. Addressing systemic biases and providing resources for underserved populations are critical to improving maternal health outcomes.
What are ‘late maternal deaths’ and why do they matter?
‘Late maternal deaths’ occur from 42 days to one year after pregnancy and represent a significant portion of pregnancy-related deaths. Addressing these deaths is important because it reflects the need for continuous healthcare support beyond the initial postpartum period, which is often overlooked in the current maternal health framework.
How has the COVID-19 pandemic affected pregnancy-related mortality rates?
The COVID-19 pandemic likely contributed to increased pregnancy-related mortality rates, particularly as the data showed a spike in 2021. The pandemic exacerbated existing health disparities and put additional strain on healthcare systems, affecting access to necessary prenatal and postpartum care.
What innovative solutions can help reduce pregnancy-related deaths?
Innovative solutions to reduce pregnancy-related deaths may include enhancing telehealth services, implementing community health programs, and improving access to quality prenatal and postpartum care, especially in high-risk populations. Developing policies that support these initiatives can help improve pregnancy outcomes and reduce mortality rates.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| High Maternal Mortality Rate | The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, with significant rises between 2018 and 2022. |
| Preventable Deaths | More than 80% of pregnancy-related deaths are preventable according to the latest studies. |
| Disparities in Mortality Rates | There are large disparities by state, race, and ethnicity; with American Indian and Alaska Native women having the highest mortality rates. |
| Cardiovascular Disease as Leading Cause | Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths, representing over 20% of cases. |
| Importance of Postpartum Care | Late maternal deaths (deaths occurring between 42 days and 1 year after pregnancy) account for nearly a third of maternal mortality. |
| Need for Better Infrastructure | Investment in public health infrastructure is critical to reduce pregnancy-related deaths and improve maternal health outcomes. |
Summary
Pregnancy-related deaths in the United States are a growing concern, highlighting a critical need for improved maternal care. The research indicates that these deaths are predominantly preventable, yet significant disparities in maternal mortality rates persist across different demographics. Addressing the systemic issues within the healthcare infrastructure and promoting comprehensive care throughout the pregnancy and postpartum periods are essential steps toward reducing these deaths. Without a concerted effort to enhance policies and invest in healthcare services, the alarming trend in pregnancy-related deaths is likely to continue.